
Shadow DOM 是四大网络组件标准之一,提供 CSS 作用域、DOM 封装和组合(Composition) 等优势,构建自定义元素。
什么是 Shadow DOM
浏览器在解析网页文档的时候,会将 HTML 标签转换成节点,为了保持页面的层次结构,这些节点构成一个节点树,这个结构就是 DOM(文档对象模型)。DOM 将文档作为一个结构化的节点组以及包含属性和方法的对象,是 HTML 的编程接口,我们通常会使用 JavaScript 来访问操纵 DOM。
这段 JavaScript 代码执行后会生成如下的 DOM 结构:
那什么是 Shadow DOM 呢❓
Shadow DOM 为 Web 组件中的 DOM 和 CSS 提供了封装。Shadow DOM 使得这些东西与主文档的 DOM 保持分离。Shadow DOM 与普通的 DOM 的区别是:
👉 通常创建新的 DOM 节点附加到其他 DOM 元素上,就会成为其子节点(元素);但借助 Shadow DOM,可以创建一个 DOM 树附加到其他元素上,这个 DOM 树并非其子节点(元素),其拥有自身的作用域范围,这个 DOM 树称为:shadwo tree。被附加的元素称为 shadow host,这个 DOM 树称为 shadow root。
You can think of shadow DOM as a scoped subtree inside your element.
|
|
- 为元素创建 shadow DOM,调用
element.attachShadow() - 通过
shadowRoot属性获取元素附加的 Shadow DOM - 通过 shadow root 的
host属性获取其附属的元素
❗️注意:并非所有元素都可以调用 element.attachShadow() 为其创建添加 Shadow DOM,因为有些元素浏览器已经为其添加了 Shadow DOM,例如 <textarea> <input>;而还有些元素为其添加 Shadow DOM 是没有意义的,例如 <img>。
|
|
在创建自定义元素时,Shadow DOM 尤其有用。使用 Shadow DOM 来分隔元素的 HTML、CSS 和 JS,从而生成一个组件。
注意 Shadow DOM 中的 CSS 规则的作用域仅限于 <x-tag>。
组合和 slot
组合是 shadow DOM 最难理解的功能之一,但可以说是最重要的功能。
light DOM 和 shadow DOM
light DOM
使用组件的用户编写的标记,DOM 元素的实际子元素,该子元素不在组件的 shadow DOM 之内,这就是 light DOM。
其中 image 和 span 即是 button 的 light DOM。
shadow DOM
组件作者编写的标记,它定义组件的内部结构,作用域 CSS 等
Flattened DOM tree
浏览器将用户的 light DOM 分布到 shadow DOM 中,渲染成一颗 DOM 树,这个过程称为 flattening the tree,这棵树称为扁平树 Flattened DOM tree。 扁平树也是我们在 DevTools 中最终看到的树以及在页面上渲染的结果。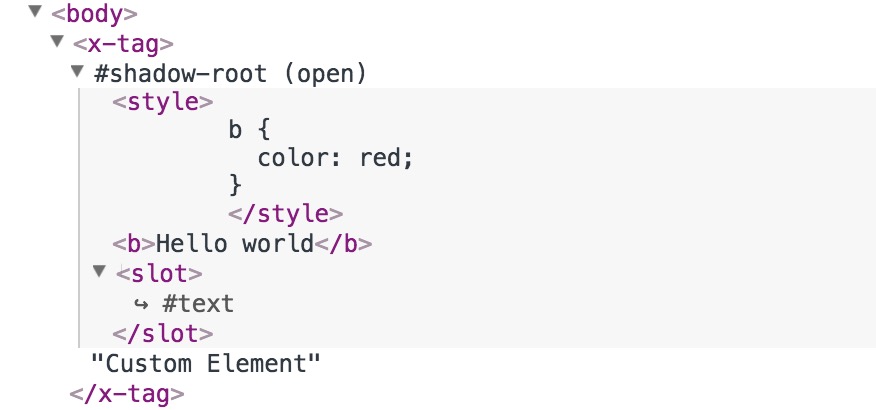
元素
Shadow DOM 使用 <slot> 元素将 light DOM 树组合到 shadow DOM 中,形成一颗 DOM 树。
Slot 相当于是组件内部的占位符,通过定义一个或者多个 <slot>,可以将外部的标记引入到组件 shadow DOM 中进行渲染,相当于“跨域”了 shadow DOM 的边界,这些引入到 shadow DOM 中的元素被称为分布式节点 distributed nodes。注意:slot 实际上并不移动这些分布式节点,它们在 shadow DOM 内部的其他位置进行渲染。
组件可在其 shadow DOM 中定义零个或多个 slot。Slot 可以为空,或者提供回退内容(fallback content),如果用户不提供 light DOM 内容,slot 会将对其备用内容进行渲染。
|
|
还可以创建命名 slot (named slots),使用组件的用户通过名称找到特定的 slot。
设定样式
shadow DOM 最有用的功能是作用域 CSS:
- 外部页面中的 CSS 选择器不会应用于组件内部。
- 组件内部定义的样式也不会渗出,它们的作用域仅限于宿主元素(shadow host)
通过选择器设定样式
使用 :host 为组件为自身设定样式
需要注意:外部页面中为组件设定的样式比 :host 规则具有更高的优先级,也就是说,对于组件自身,外部样式优先,用户可以在外部设置组件自身的样式。
使用 :host(<selector>) 匹配组件自身不同状态
通过 :host(<selector>) 匹配不同状态,对组件自身或者内部节点设定不同的样式
使用 :host-context(<selector>) 匹配任意父级
使用 :host-context(<selector>) 主要用于根据组件所在的环境进行主题化(基于情境设定样式),例如设置白天模式,夜晚模式,我们在 <html> 或者 <body> 设定不同的 class,而组件通过 :host-context(<selector>) 就可以匹配到
|
|
使用 ::slotted(<compound-selector>) 匹配分布到
使用 ::slotted(<compound-selector>) 为分布式节点设定样式
组件的 shadow DOM 可为用户的 <h2> 和 .title 设定样式:
需要注意的是:
① 使用 ::slotted(<compound-selector>) 只能为分布节点的顶级节点设置样式。
② slot 并不会移动 light DOM,light DOM 节点分布到 shadow DOM 中后,slot 会对其 DOM 进行渲染,样式设置,但是节点实际还是留在原处。如果外部对 light DOM 设置了样式,那么外部样式将会覆盖 shadow DOM 中通过 ::slotted(<compound-selector>) 设置的样式,具有较高优先级。
从外部为组件设定样式
有几种方法可从外部为组件设定样式:最简单的方法是使用标记名称作为选择器
为组件自身设定样式
从外部为组件自身设定样式最简单的方法,就是使用组件标签名称作为选择器,设置 CSS 样式。
注意:外部样式总是优先于在 shadow DOM 中定义的样式。例如,如果用户在组件外部编写:fancy-tabs { width: 500px; },它将优先于组件的规则::host { width: 650px;}。
为组件内部元素设定样式
在组件外部,我们不能直接通过选择器对组件内的元素设置样式。组件提供自定义属性 custom properties,相当于是样式占位符,外部通过对自定义属性 custom properties 来调整组件内部元素的样式。
例如,<fancy-tabs> 可让用户替换背景颜色:
在其 shadow DOM 内部:
在本例中,该组件将使用 black 作为背景值,因为用户指定了该值。 否则背景颜色将采用默认值 #9E9E9E。
其他
避免在组件中创建 closed shadow root
shadow DOM 的另一情况称为闭合模式。创建closed shadow DOM tree 后,在外部无法通过 JavaScript 访问组件的内部 DOM。这与 <video> 等原生元素工作方式类似,JavaScript 无法访问 <video> 的 shadow DOM,因为浏览器使用closed shadow root来实现。
|
|
关于 slot 的 API
slotchange 事件
当 slot 的分布式节点发生变化时,slotchange 事件会触发。例如,当用户从 light DOM 中添加/移除子项时。
|
|
注:当组件的实例首次初始化时,slotchange 不触发。
查看 slot 中渲染的元素
调用 slot.assignedNodes() 可查看 slot 正在渲染哪些元素;该方法中传入 {flatten: true} 选项将返回 slot 的备用内容fallbcak content(前提是没有分布任何节点)。
| 用法 | 调用 | 结果 |
|---|---|---|
<button is="better-button">My button</button> |
slot.assignedNodes(); | [text] |
<button is="better-button"></button> |
slot.assignedNodes(); | [] |
<button is="better-button"></button> |
slot.assignedNodes({flatten: true}); | [fallback content] |
查看元素渲染在哪个 slot 中element.assignedSlot 将告诉您元素分配到组件的哪个 slot。
Shadow DOM 事件模型
当事件从 shadow DOM 中触发时,其目标 target 为维持 shadow DOM 的封装,不暴露 shadow DOM 中的内容元素,会进行重置 retarget,看起来事件是来自组件本身,而不是组件中 shadow DOM 中的内容元素。
大部分事件都会跨过 shadow DOM 边界,向外传播:
- 聚焦事件:blur、focus、focusin、focusout
- 鼠标事件:click、dblclick、mousedown、mouseenter、mousemove,等等
- 滚轮事件:wheel
- 输入事件:beforeinput、input
- 键盘事件:keydown、keyup
- 组合事件:compositionstart、compositionupdate、compositionend
- 拖放事件:dragstart、drag、dragend、drop,等等
对于 mode 为 open 的 shadow DOM,事件回调中,调用 event.composedPath() 将返回事件向上传播经过的节点路径。
对于组件内的自定义事件,不会传播出 shadow DOM,除非事件创建时指定 composed: true
如果 composed: false(默认值),用户无法在组件外部侦听到这个自定义事件。
参考链接
本文主要是阅读 Shadow DOM v1: Self-Contained Web Components 后,理解整理而来。
英文原文:Shadow DOM v1: Self-Contained Web Components
中文翻译:Shadow DOM v1:独立的网络组件